Understanding the Concept of Succession
Before we delve into the process of succession in an ecosystem, it's important to understand what the term 'succession' means. In ecology, succession is the process of change in the species structure of an ecological community over time. The time scale can be decades or even millions of years. In succession, the life progresses naturally towards the most diverse, complex, and stable state.
Types of Succession
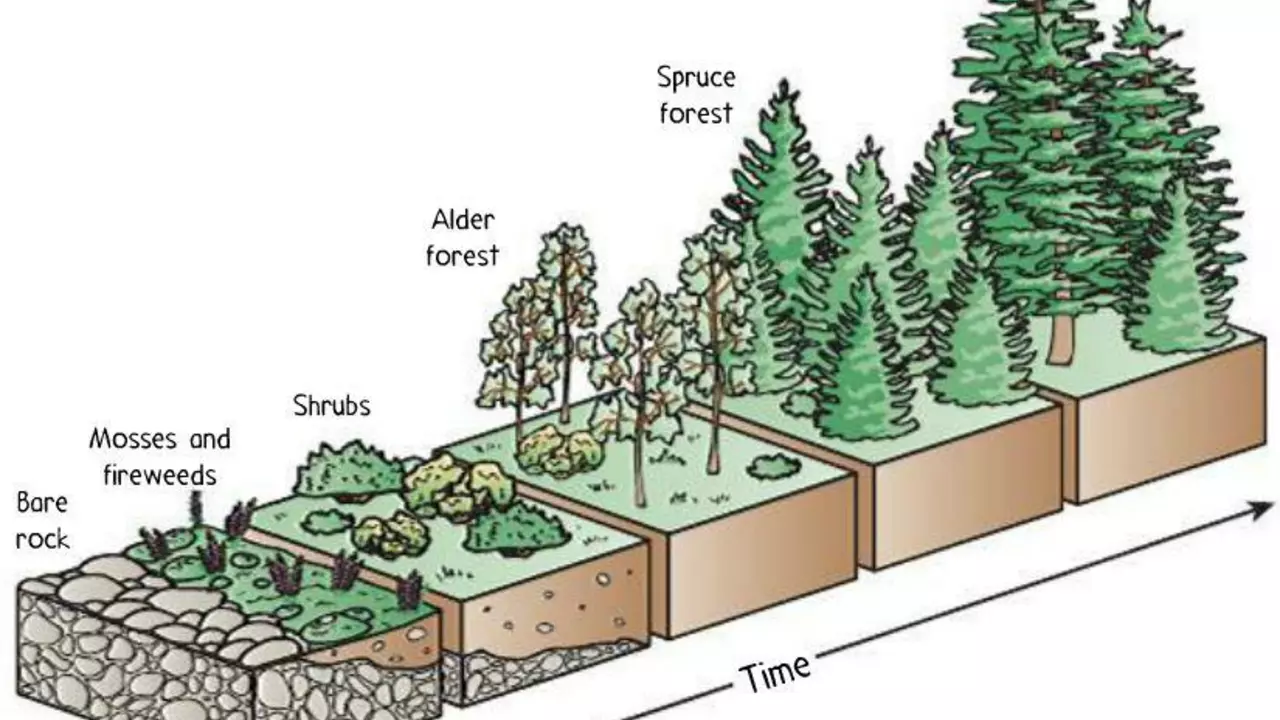
As we explore the succession process, it's vital to note that there are two main types of succession, primary and secondary, which are classified based on the condition of the environment. Primary succession occurs in an environment that is initially void of life, such as a new volcanic island or an area exposed by a retreating glacier. Secondary succession, on the other hand, happens in areas where a community that previously existed has been removed; this is typically the result of an event like a fire, hurricane, or logging.
Phases of Succession
Regardless of the type, succession usually progresses through a series of phases. These phases include the pioneer stage, establishment stage, competition stage, climax stage, and potential destabilization. Each of these phases plays a crucial role in the succession process and is characterized by different types of species and interactions.
Role of Pioneer Species
Pioneer species are the first to colonize barren environments in the primary succession process. They are often hardy species which can tolerate harsh conditions and pave the way for other species to settle. They create new habitats, modify the environment, and gradually make it more hospitable for other species to thrive.
Establishment Stage and Competition
Following the pioneer stage, we have the establishment stage where plants begin to colonize the area. These plants eventually lead to competition for resources. The survival of the fittest concept greatly applies here as only the species best adapted to the prevailing conditions will survive.
Climax Stage
When the ecosystem becomes mature and stable, it has reached what is known as the climax stage. This stage is characterized by a rich diversity of species. The community structure is complex, with a high degree of organization and stratification.
Potential Destabilization
After the climax stage, there's a potential for destabilization. Natural disturbances or changes in environmental conditions may disrupt the climax community, starting the succession process all over again. This is known as secondary succession.
Role of Disturbances
Disturbances play a crucial role in shaping the path of succession. They can cause large changes in the ecosystem, paving the way for secondary succession. Examples of disturbances include fires, storms, human activities and diseases.
Importance of Succession in Ecosystems
Finally, it's important to understand the significance of succession in ecosystems. Succession plays a crucial role in enhancing biodiversity, creating new habitats, and maintaining ecosystem health. It's a natural process that ensures the continuous evolution and adaptation of species to changing environmental conditions.
Human Impact on Succession
Lastly, it's worth considering how human activities can influence the process of succession. Humans can speed up, slow down, or even prevent succession through activities like deforestation, pollution, urbanization, and introduction of invasive species. Understanding our impact can help us make more informed decisions about how we interact with our environment.

Write a comment